
Welcome to CivilGEO Knowledge Base
Welcome to CivilGEO Knowledge Base

Welcome to CivilGEO Knowledge Base
Welcome to CivilGEO Knowledge Base
The canopy component represents the presence of plants in the landscape. Plants intercept precipitation, reducing the amount of precipitation that arrives at the ground surface. Intercepted water evaporates between storm events. Plants also extract water from the soil in a process called transpiration. Evaporation and transpiration are often combined as evapotranspiration.
In GeoHECHMS, the Simple Canopy method is used to compute the precipitation loss due to evapotranspiration. Selecting a canopy method is optional and generally used for continuous simulation applications. If no canopy method is selected, the subbasin will not compute any losses due to evapotranspiration and all precipitation will be treated as direct precipitation.
The Simple Canopy method provides a simple representation of a plant canopy. In this method, all the precipitation is intercepted until the canopy storage capacity is full. Once the canopy storage is filled, all further precipitation falls to the surface or directly to the soil if no surface representation is included. All potential evapotranspiration will be used to empty the canopy storage until the water in storage has been eliminated. The potential evapotranspiration is multiplied by the crop coefficient to determine the amount of evapotranspiration from canopy storage and later from surface and soil components. Only after the canopy storage has been emptied will the surface, and soil components, use the unused potential evapotranspiration.
Note that the Dynamic Canopy and Gridded Simple Canopy methods are not supported in GeoHECHMS since they are mostly used by researchers or the Army Corps of Engineers.
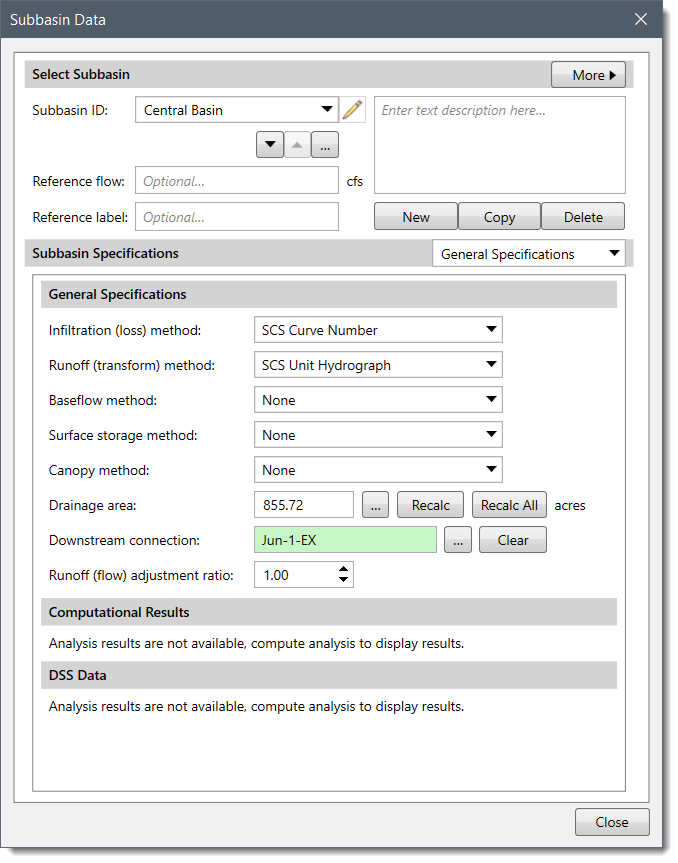
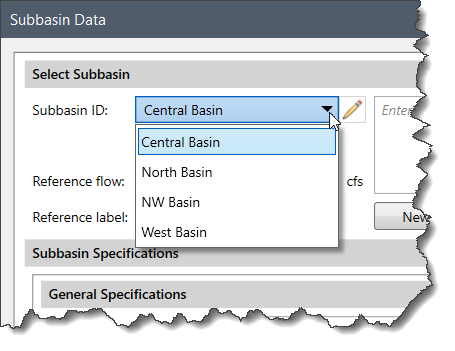
Follow the steps given below to select a canopy method:
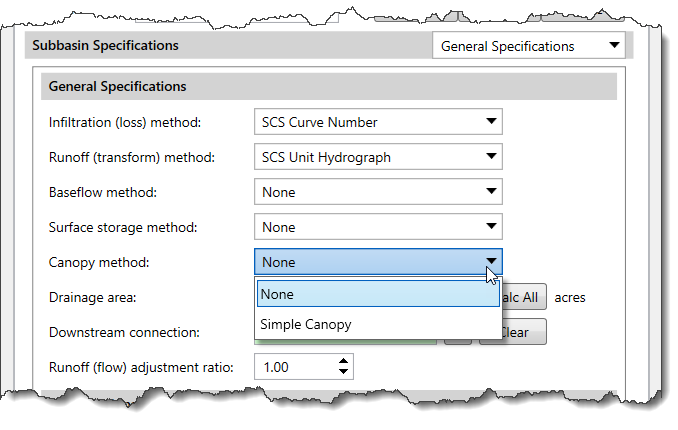
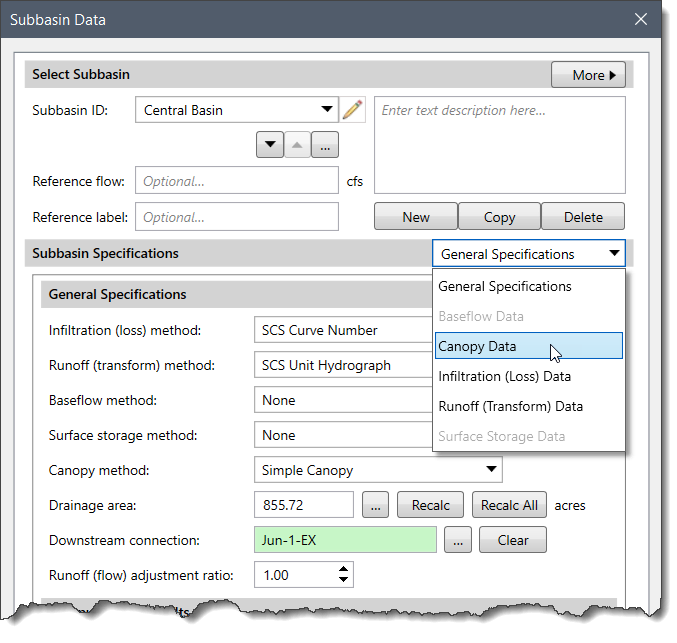 Note that the Canopy Data option will be grayed out (i.e., unavailable) when None is selected for the canopy method.
Note that the Canopy Data option will be grayed out (i.e., unavailable) when None is selected for the canopy method.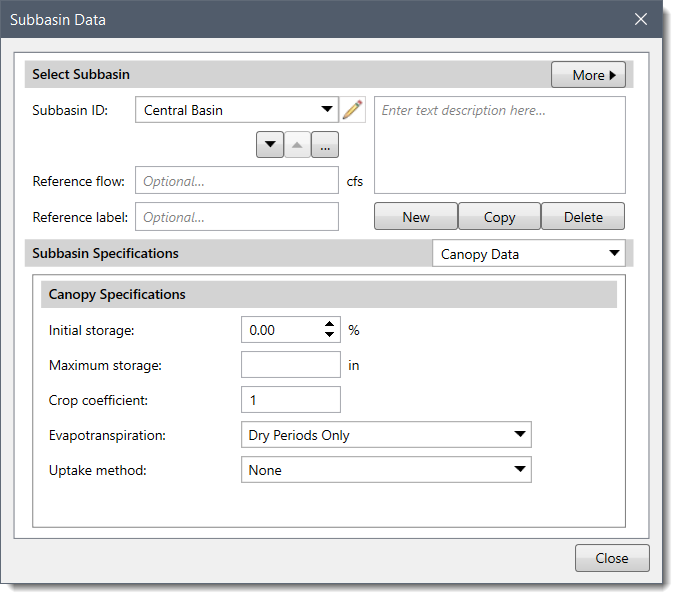
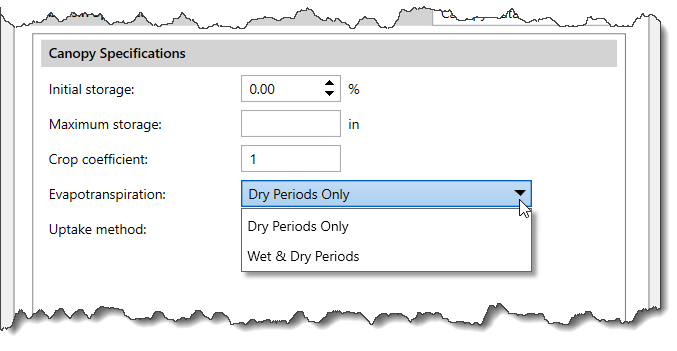 Note that the choice for simultaneous precipitation and evapotranspiration can improve results when using a long interval.
Note that the choice for simultaneous precipitation and evapotranspiration can improve results when using a long interval.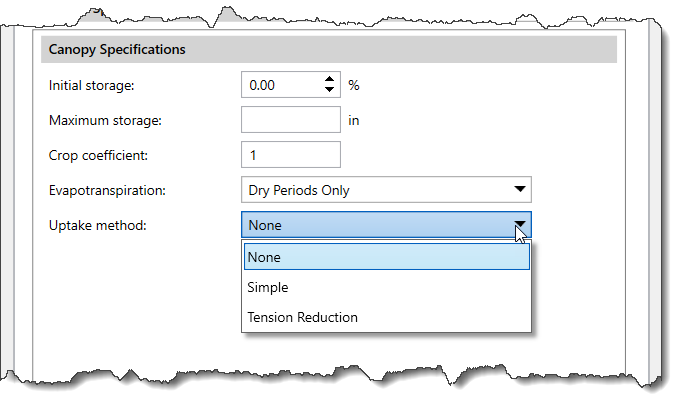 The Simple method extracts water at the potential evapotranspiration rate and can be used with the deficit constant or soil moisture accounting infiltration loss methods. In contrast, the Tension Reduction method can be used with the soil moisture accounting method and extracts water at the potential evapotranspiration rate from the gravity zone, but reduces the rate when extracting from the tension zone. When None is selected, there will be no soil water extraction. To learn how to select an infiltration method for a subbasin, refer to this article in our knowledge base.
The Simple method extracts water at the potential evapotranspiration rate and can be used with the deficit constant or soil moisture accounting infiltration loss methods. In contrast, the Tension Reduction method can be used with the soil moisture accounting method and extracts water at the potential evapotranspiration rate from the gravity zone, but reduces the rate when extracting from the tension zone. When None is selected, there will be no soil water extraction. To learn how to select an infiltration method for a subbasin, refer to this article in our knowledge base.If Kinematic Wave is selected as the runoff method, then the Canopy Data panel will be divided into two surface area sections as shown below.
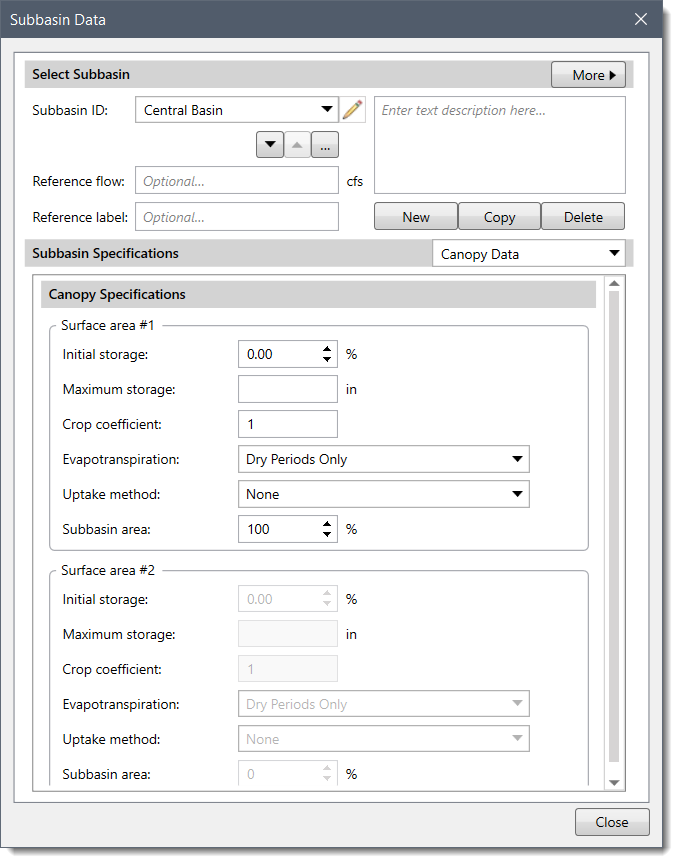
By default, Surface area #1 is active with the Subbasin area field set as 100 %. However, changing the Subbasin area in Surface area #1 activates the Surface area #2 fields.
In addition, changing the Subbasin area in either Surface area #1 or Surface area #2 adjusts the Subbasin area in the other counterpart such that the total Subbasin area adds to 100%.
To learn how to select a runoff method for a subbasin, refer to this article in our knowledge base.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
 1-800-301-02-955
1-800-301-02-955
 608-729-5100
608-729-5100
(US and Canada)
 [email protected]
[email protected]
 +1 608-729-5100
+1 608-729-5100
CivilGEO India
Graphix Tower, A-13 A
3rd Floor, Sector 62
Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201309
IndiaTel:
1-800-301-02-955 or
+91 022-3831-8601
CivilGEO United States
8383 Greenway Blvd
6th Floor
Middleton, WI 53562
USATel:
608-729-5100 or
800-488-4110
Copyright © CivilGEO, Inc. All rights reserved. The CivilGEO logo, “GeoHECHMS”, “GeoHECRAS”, and “Ready To Engineer” are registered trademarks of CivilGEO,
Inc. All other brands, company names, product names or trademarks belong to their respective holders.
We use cookies to give you the best online experience. By agreeing you accept the use of cookies in accordance with our cookie policy.
When you visit any web site, it may store or retrieve information on your browser, mostly in the form of cookies. Control your personal Cookie Services here.
The ZoomInfo WebSights snippet drops three cookies to track Unique Visits:
1. _pxhd - Related to the Perimeter X security layer (Perimeter X isused to prevent bot attacks).
2. _cfduid - Related to the CloudFlare security layer (CloudFlare is the Network Security protocol that ZoomInfo uses to orchestrate the rate limiting rules).
3. visitorId - This is how WebSights identifies recurring visitors








