
Welcome to CivilGEO Knowledge Base
Welcome to CivilGEO Knowledge Base

Welcome to CivilGEO Knowledge Base
Welcome to CivilGEO Knowledge Base
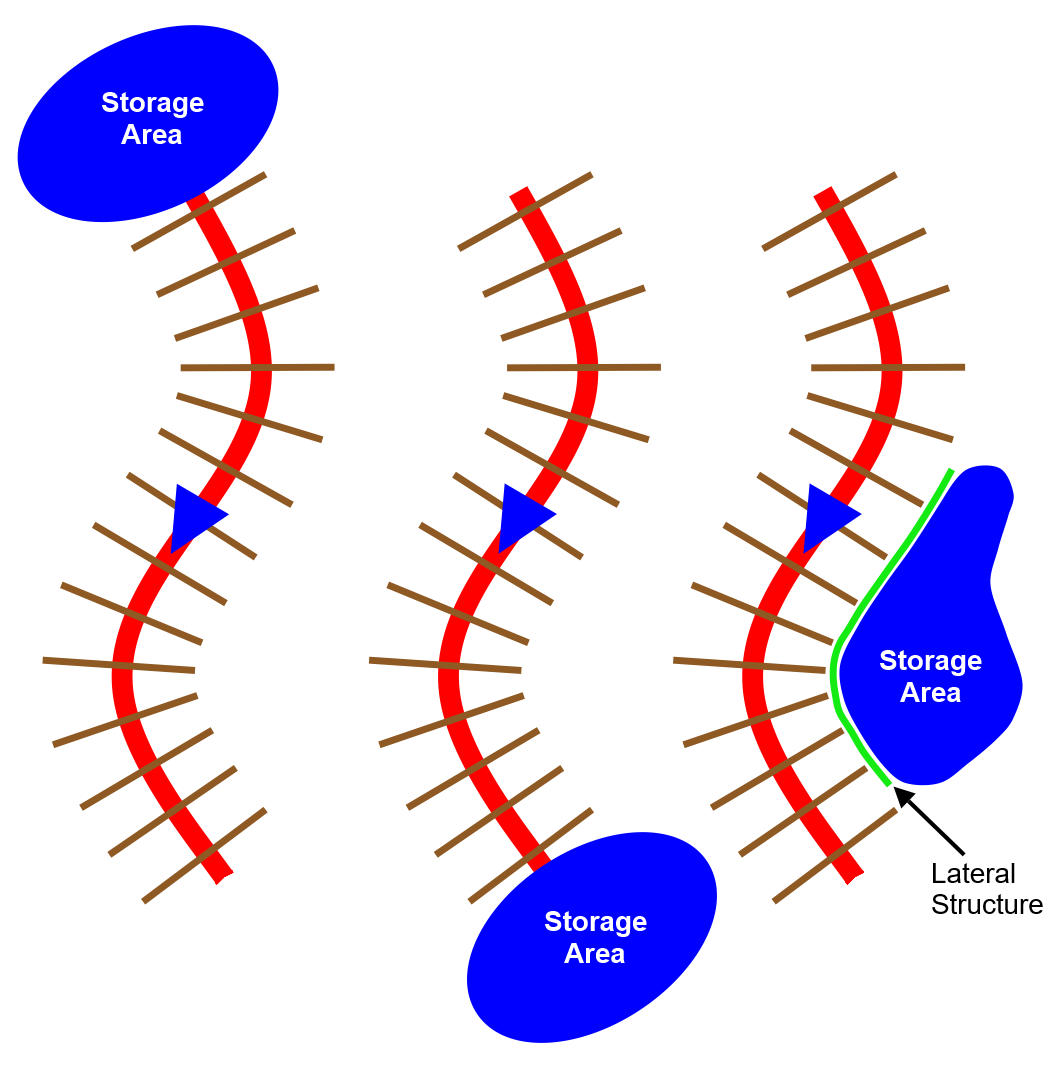
Upstream and downstream boundaries of a river reach can be connected to a reservoir, lake, or other types of large water bodies. These water bodies are called storage areas in HEC-RAS.

In addition, off-channel ponding areas that exchange water with the adjacent river can be modeled as storage areas. A lateral structure is required to exchange water between the river and the storage area.

The following diagram represents the three different situations where a storage area can be connected to a river reach.
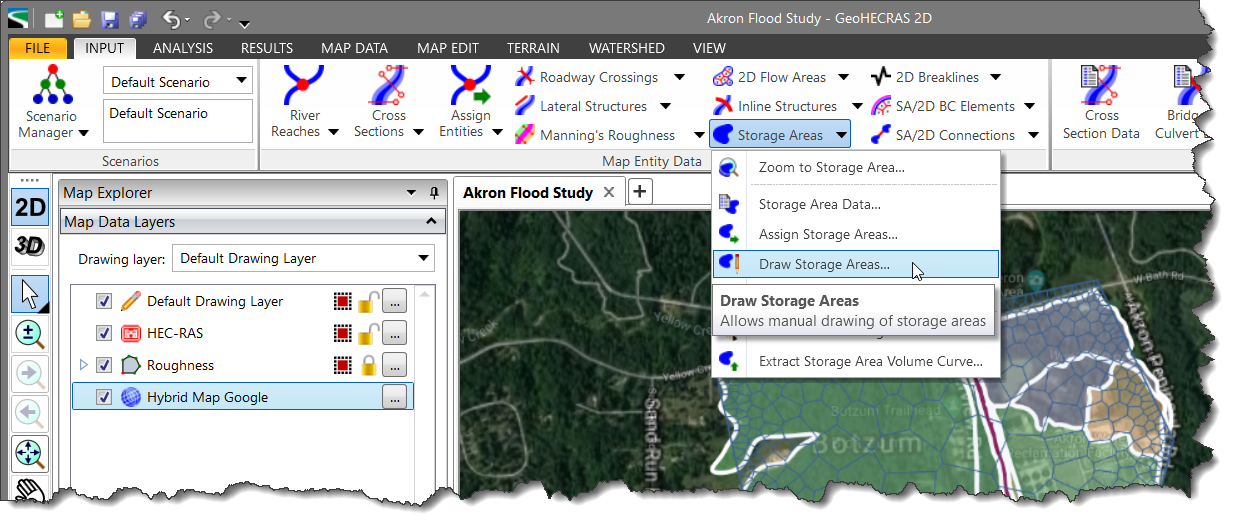
HEC-RAS storage areas can be defined by either drawing or assigning the boundary using the following commands:
Existing storage areas can also be georeferenced to a more accurate outline representation of the water body assigned.
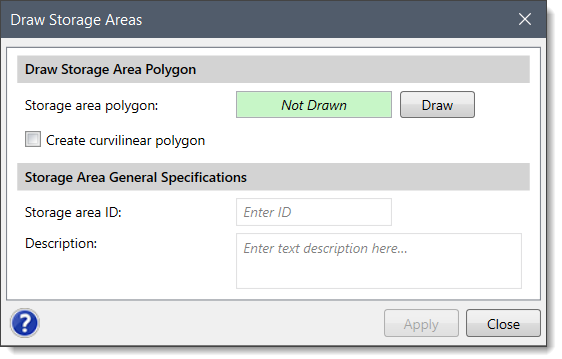
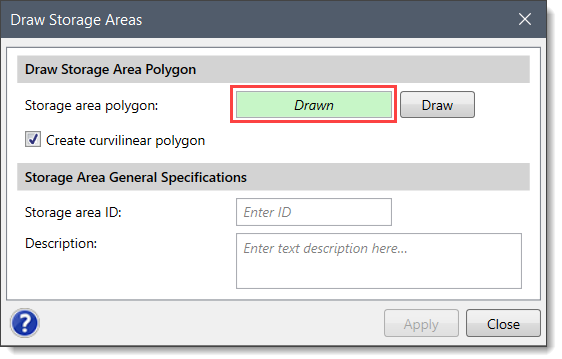
HEC-RAS storage areas can be defined by drawing the boundary of the reservoir, lake, or ponded area using the Draw Storage Areas command.
Follow the steps below to draw a storage area:
![[Draw] button](/wp-content/uploads/sites/25/2018/09/Defining-HEC-RAS-Storage-Areas-Img-6.png)
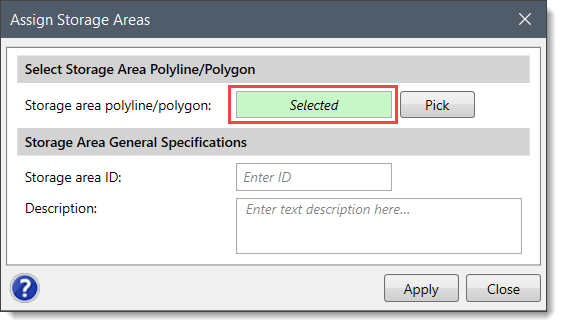
HEC-RAS storage areas can be defined by assigning an already drawn polyline or polygon as the boundary of the reservoir, lake, or ponded area using the Assign Storage Areas command.
Follow the steps below to assign a storage area:
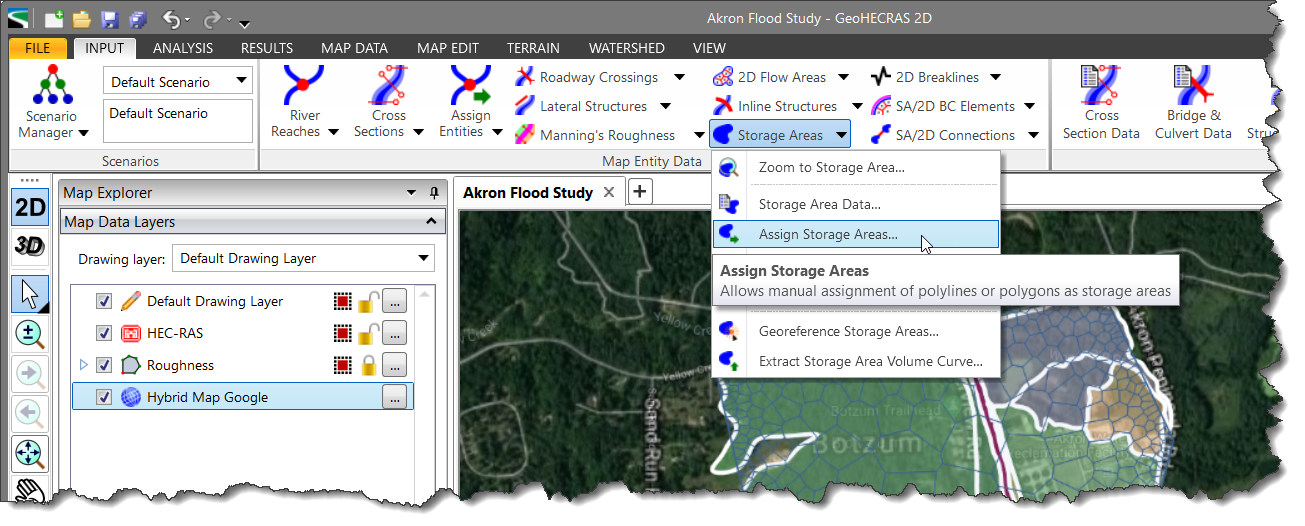
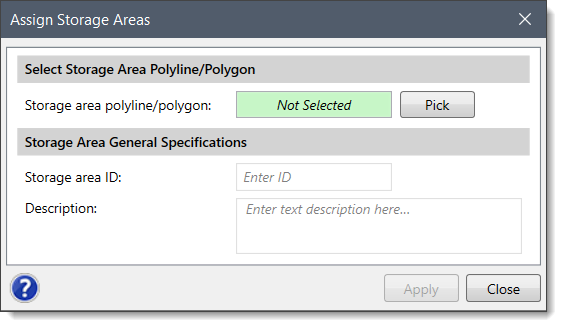
![[Pick] button](/wp-content/uploads/sites/25/2018/09/Defining-HEC-RAS-Storage-Areas-Img-10.png)
The Georeference Storage Areas command is used to manually georeference each of the storage areas to the background base map displayed in the Map View. Refer to this article in our knowledge base to learn how to use the Georeference Storage Areas command.
Existing storage area boundaries can be revised using the Reshape Polygon command. Refer to this article in our knowledge base to learn how to use the Reshape Polygon command.
GeoHECRAS software can be used to calculate how much storage area a site has and what volume it holds. After defining the storage area boundary, the software automatically computes the fixed area “footprint” that the storage area occupies to define the storage volume. This method works well in situations when the storage area does not change with depth. However, defining the storage volume in this manner results in an inaccurate representation of the storage volume for the regions where the storage area varies considerably with the elevation change. For regions where a more accurate representation of the storage volume is required, the user can extract the storage volume from the terrain model if the bathymetry of the storage area is contained in the terrain model.
Refer to this article in our knowledge base to learn how to extract storage area volume from the terrain model.
 1-800-301-02-955
1-800-301-02-955
 608-729-5100
608-729-5100
(US and Canada)
 [email protected]
[email protected]
 +1 608-729-5100
+1 608-729-5100
CivilGEO India
Graphix Tower, A-13 A
3rd Floor, Sector 62
Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201309
IndiaTel:
1-800-301-02-955 or
+91 022-3831-8601
CivilGEO United States
8383 Greenway Blvd
6th Floor
Middleton, WI 53562
USATel:
608-729-5100 or
800-488-4110
Copyright © CivilGEO, Inc. All rights reserved. The CivilGEO logo, “GeoHECHMS”, “GeoHECRAS”, and “Ready To Engineer” are registered trademarks of CivilGEO,
Inc. All other brands, company names, product names or trademarks belong to their respective holders.
We use cookies to give you the best online experience. By agreeing you accept the use of cookies in accordance with our cookie policy.
When you visit any web site, it may store or retrieve information on your browser, mostly in the form of cookies. Control your personal Cookie Services here.
The ZoomInfo WebSights snippet drops three cookies to track Unique Visits:
1. _pxhd - Related to the Perimeter X security layer (Perimeter X isused to prevent bot attacks).
2. _cfduid - Related to the CloudFlare security layer (CloudFlare is the Network Security protocol that ZoomInfo uses to orchestrate the rate limiting rules).
3. visitorId - This is how WebSights identifies recurring visitors








